
What is the difference between Protestant and Catholic in Christianity? Catholicism and Protestantism
فرست محتوا
- 1 What is the difference between Protestant and Catholic in Christianity? A comprehensive study of Catholicism and Protestantism
- 1.1 General Differences between Catholicism and Protestantism
- 1.2 Structural and Architectural Differences between Protestant and Catholic Churches
- 1.3 Historical Analysis of Catholic and Protestant Differences
- 1.4 Catholic and Protestant Approaches to Biblical Interpretation
- 1.5 The Concept of Good Works in Protestantism and Catholicism
- 1.6 The Role of Saints and Intercession in Catholicism and Protestantism
- 1.7 Different Views on Priests and Church Leadership
- 1.8 Social and Cultural Differences between Catholics and Protestants
- 1.9 The Impact of Protestant Reformation on Art and Culture
- 1.10 Historical and Cultural Analysis of Protestant and Catholic Movements
- 1.11 The Role of Women in Religious Movements
- 1.12 Influential Narratives and Stories in the History of Catholicism and Protestantism
- 1.13 Specific Rituals and Ceremonies in Each Branch
- 1.14 Analysis of Social Movements Related to Protestant and Catholic
- 1.15 The Role of Art and Architecture in Explaining Protestant and Catholic Differences
- 1.16 The Role of Music in Protestant and Catholic Churches
- 1.17 Religious Movements and Their Impact on the Modern World
- 1.18 Philosophical and Theological Differences between Catholic and Protestant
- 1.19 Comparison Table of Movements and Cultural Impacts
- 1.20 Long-term Effects of Protestant and Catholic Reformations
- 1.21 The Role of Economy in the Development of Catholicism and Protestantism
- 1.22 The Connection between Education and Religious Differences
- 1.23 Differences in Attitudes towards Science and Philosophy
- 1.24 Comparison Table of Economic, Educational, and Scientific Impacts
- 1.25 Conclusion
- 1.26 Frequently Asked Questions about the Difference between Protestant and Catholic
- 1.26.1 1. What are the fundamental differences between Protestant and Catholic?
- 1.26.2 2. What is the role of the Pope in the Catholic Church and do Protestants accept the Pope?
- 1.26.3 3. Are there differences in how religious ceremonies are conducted between Protestants and Catholics?
- 1.26.4 4. How do Catholics and Protestants view salvation and redemption?
- 1.26.5 5. Do Protestants and Catholics differ in their interpretation of the Bible?
- 1.26.6 6. Do Catholics and Protestants conduct marriage ceremonies in the same way?
- 1.26.7 7. Do Catholics and Protestants have different views on priests?
- 1.26.8 8. Do Protestants accept the concept of intercession by saints?
- 1.26.9 9. What is the view of Catholics and Protestants on the Virgin Mary?
- 1.26.10 10. What is the difference between Protestants and Catholics regarding good works?
- 1.26.11 11. Is the structure of the Catholic and Protestant churches the same?
- 1.26.12 12. What is the role of the Pope in the Catholic Church and do Protestants have a similar position?
- 1.26.13 13. What are the differences in religious rituals between Catholics and Protestants?
- 1.26.14 14. Do Protestants and Catholics differ in their views on life after death?
What is the difference between Protestant and Catholic in Christianity? A comprehensive study of Catholicism and Protestantism
Christianity is one of the largest religions in the world with followers from all over the globe. The two main branches of this religion are Catholicism and Protestantism. Although both branches believe in the fundamental teachings of Jesus Christ and share many commonalities, there are also significant differences between them. These differences are observed not only in doctrinal issues but also in church structures, rituals, and views on salvation. In this article, we will comprehensively examine these differences and address common questions in this area.
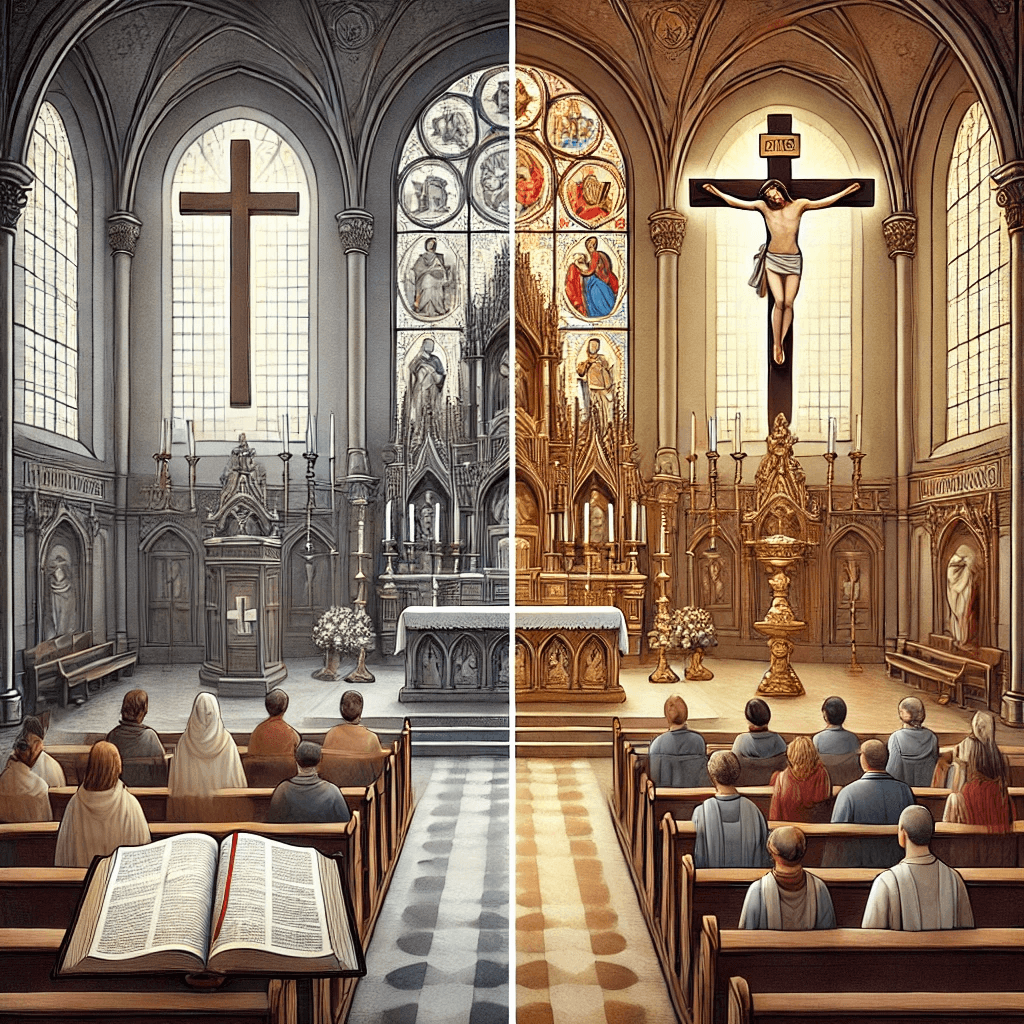
General Differences between Catholicism and Protestantism
The Catholic and Protestant churches are the two main branches of Christianity, each with its own specific views and teachings. The fundamental differences between these two branches are evident not only in church structure but also in doctrinal principles, religious rituals, and biblical interpretation. While Catholics emphasize the tradition of the church and the authority of the Pope, Protestants believe that only the Bible is the ultimate reference for faith. These differences also play a key role in the way salvation is understood, the interpretation of rituals, and the individual’s relationship with God. The table below summarizes the important differences between Catholicism and Protestantism.
| Subject | Catholicism | Protestantism |
|---|---|---|
| Religious Authority | The Pope and the Catholic Church, along with the Bible, are the main authorities. | Only the Bible is recognized as the ultimate source of truth (Sola Scriptura). |
| Church Structure | The Catholic Church has a hierarchical structure with the Pope at its head. The church operates based on an ancient and organized tradition. | The structure of Protestant churches is very diverse and includes both hierarchical and democratic churches. |
| Religious Rituals | Rituals such as the Eucharist, baptism, confession, and holy matrimony are of great importance. | Rituals vary by denomination and are conducted more simply than Catholic rituals. Some denominations, such as Lutherans and Anglicans, celebrate the Eucharist, but many others consider this ritual less formal. |
| Salvation | Salvation is achieved through faith, good works, and the performance of rituals. | Salvation is obtained solely through faith in Jesus Christ (Sola Fide). |
| Role of Priests | Priests act as intermediaries between God and believers and perform sacred rituals. | The role of priests is as teachers or guides, and direct mediation does not play a role. |
| Virgin Mary | Catholics regard the Virgin Mary as the holy mother of Jesus Christ and hold her in special esteem. | Protestants accept the Virgin Mary as the mother of Jesus Christ, but do not attribute any special sanctity or status to her. |
| Concept of Salvation | Catholics believe that salvation is possible through the performance of sacred rituals and adherence to Christian moral principles. | Protestants emphasize the principle of Sola Fide (salvation only through faith) and believe that a person can only be saved by faith in Jesus Christ and the grace of God. |
Structural and Architectural Differences between Protestant and Catholic Churches
One of the main aspects of the difference between Protestant and Catholic churches is their church structure and architectural design. These differences reflect the different approaches of each branch of Christianity to the concept of worship, the sanctity of space, and the spiritual connection with God.
1. Catholic Churches
Catholic churches are typically recognized for their Gothic and Baroque architecture, which clearly represents luxury, grandeur, and sanctity. Notable features of Catholic churches include:
- Large and Decorated Spaces: Catholic churches have intricate interior designs, with religious murals, statues of saints, and the use of stained glass (stained glass) aimed at creating a sense of divine glory and majesty.
- Altar and Ritual Ceremonies: In the Catholic Church, the altar is the central part, usually covered with heavy and golden decorations. This altar is used for performing sacred rituals such as the Eucharist.
- Church Bells: The tall towers of Catholic churches usually have large bells that are used to announce the time for worship and religious ceremonies.
- Role of the Pope and Saints: Catholic churches typically feature images and symbols of the Pope, saints, and the Virgin Mary, which are frequently seen on the church walls and indicate the high status of these individuals in the Catholic faith.
2. Protestant Churches
In contrast, Protestant churches tend to be simpler and less decorated. This simplicity reflects the Protestant philosophy that emphasizes avoiding luxury and focusing on direct worship of God.
- Simple and Functional Spaces: Protestant churches usually have much simpler designs. White walls, large open spaces, and the absence of statues or images of saints are notable features of these churches. The main goal is to focus on the individual’s spiritual connection with God without external intermediaries.
- Non-use of Images and Symbols: Unlike Catholic churches, Protestant churches tend to avoid the use of religious images, stained glass, or sacred statues. This is a sign of their belief in simplicity and avoidance of any luxuries that might distract believers from true worship.
- Communion Table instead of Altar: In most Protestant churches, a simple table is placed for the Eucharist instead of a lavish altar. This change reflects a lesser importance placed on complex rituals and more on the individual connection with God.
- Congregation-Centered Space: Protestants emphasize active participation of the congregation. As a result, Protestant churches often have designs that invite the congregation to actively participate in worship services; including the use of forward-facing seats and the absence of spatial separation between clergy and believers.
3. Music and Worship in Churches
Music also plays an important role in the atmosphere of churches. In Catholic churches, classical music, especially organ and choral music, is an important part of worship services. In contrast, in Protestant churches, modern music and congregational hymns are more commonly used to enhance the sense of unity and active participation of the congregation.
Historical Analysis of Catholic and Protestant Differences
The history of the separation of Protestants from the Catholic Church dates back to the sixteenth century, when the Reformation movement led by Martin Luther began. Martin Luther, a German priest, called for reforms in the Catholic Church by publishing 95 Theses against church corruption and the sale of indulgences. This event marked the beginning of the separation of Protestants from Catholics and led to the formation of various branches of Protestantism such as Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican.
The religious differences between these two branches have been maintained from that time to the present. Catholics have remained committed to the principles and traditions of the ancient church, while Protestants tend to innovate in the interpretation of religion and focus more on religious individualism.
Catholic and Protestant Approaches to Biblical Interpretation
One of the most important differences between Catholicism and Protestantism is their different approaches to the interpretation of the Bible. In the Catholic Church, the interpretation of the Bible is usually done through the church institution and under the supervision of the Pope and bishops. The Catholic Church believes that the Holy Spirit helps provide correct interpretations of sacred texts through these sacred institutions. Therefore, Catholics consider personal interpretations of the Bible to be less valid and emphasize the tradition of the church.
In contrast, Protestants emphasize the principle of Sola Scriptura (only the Bible) and believe that each individual can study and interpret the Bible without the church’s mediation. This belief has led to the emergence of diverse interpretations of sacred texts among Protestants and allows each believer to personally seek religious truth. This perspective has fostered individual and creative interpretations and created significant differences in religious approaches between these two branches.
The Role of Theology in Protestant and Catholic Differences
Catholic and Protestant theologies have fundamental differences that are evident in the interpretation of religious teachings and the Bible. Protestants emphasize the principle of Sola Scriptura (only the Bible), meaning that only the Bible is the ultimate source of faith. In contrast, Catholics pay attention to both the Bible and the tradition of the church and the authority of the Pope as valid religious sources. This difference in approach has led to major differences in theological interpretations.
The Concept of Good Works in Protestantism and Catholicism
In Catholicism, good works are considered part of the path to salvation. Catholics believe that individuals must, in addition to faith in Christ, achieve perfection through good works, empathy with others, and adherence to religious teachings. In this view, good works play an important role in spiritual growth and drawing closer to God.
However, Protestants, especially followers of Martin Luther, believe that salvation is obtained only through faith in Christ and that good works have no effect on a person’s salvation. This belief, known as Sola Fide, emphasizes that faith alone is sufficient and that good works are a result of faith, not a condition for salvation. This perspective places greater emphasis on the individual relationship with God and acceptance of divine grace.
 Catholic and Protestant beliefs about saints and intercession
Catholic and Protestant beliefs about saints and intercession
The Role of Saints and Intercession in Catholicism and Protestantism
Another important difference between Catholics and Protestants is the role of saints and the concept of intercession. In the Catholic Church, saints play an important role in interceding for believers, and individuals can request prayers and intercession from them. In other words, Catholics believe that saints can act as intermediaries between God and believers. This issue is prominent in the rituals and prayers of the Catholic Church.
In contrast, Protestants believe that only God and Jesus Christ exist as intermediaries for salvation and do not accept the intercession of saints. From the Protestant perspective, each individual can communicate directly with God without the need for an intermediary and present their requests.
Different Views on Priests and Church Leadership
In the Catholic Church, priests have a special role in performing rituals and guiding the spiritual lives of believers. They serve as representatives of the church and the Pope, bearing the responsibility for the religious leadership of the community. Catholics believe that priests have attained a special grace through the sacramental ceremonies that allows them to perform sacred rituals.
However, in Protestantism, the role of priests is defined differently. Many Protestant denominations believe that any individual can have a direct relationship with God and that there is no need for an intermediary for this relationship. Therefore, in many Protestant churches, the role of the priest is more as a teacher or guide rather than a sacred intermediary.
Social and Cultural Differences between Catholics and Protestants
Catholics generally place greater emphasis on traditional values and the institution of family, and the Catholic Church acts as an institution that plays an active role in social and ethical issues. This emphasis on traditional values is evident in Catholic views on marriage, family support, and social perspectives.
On the other hand, Protestants pay more attention to individual independence and freedom in choices. This is reflected in the lifestyle of Protestants and even in their attitudes toward the institution of family and society. Protestants emphasize that each individual has the responsibility to make life decisions based on their faith and does not need formal approval or guidance from the church.
The Impact of Protestant Reformation on Art and Culture
The Protestant Reformation movement had a significant impact on Western art and culture. With the separation of Protestants from the Catholic Church, a new approach to art and religious displays emerged. While the Catholic Church used art to glorify faith and religious teachings, Protestants, especially in the beginning, used visual arts less due to fear of idolatry.
However, over time, Protestant art focused more on non-religious subjects such as landscapes, everyday life, and portraits. These changes in art reflect the deep philosophical and theological differences between these two branches of Christianity.
Historical and Cultural Analysis of Protestant and Catholic Movements
One of the significant turning points in the history of Christianity was the Reformation movement that began in the sixteenth century by Martin Luther. This movement not only led to the separation of Protestants from the Catholic Church but also brought about a major transformation in the religious and cultural attitudes of Christian communities. While the Catholic Church continued to uphold ancient traditions and focus on church hierarchy, Protestants sought reforms and emphasized religious individualism.
The Reformation Movement: From Martin Luther to John Calvin
The Reformation movement began with the publication of 95 Theses by Martin Luther. This reform led many individuals, including John Calvin, to support new ideas and facilitated the formation of various branches of Protestantism such as Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican. Luther, by criticizing the sale of indulgences and church corruption, called for a return to the core principles of Christianity, leading to profound changes in church and social structures.
The Role of Women in Religious Movements
Women played important roles in both the Catholic and Protestant branches. While in the Catholic Church, women typically served as nuns or church missionaries, in the Protestant movement, the role of women gradually expanded, allowing them to participate in religious education and even lead small local groups. Katharina von Bora, the wife of Martin Luther, is a prominent example of a woman who promoted reform ideas and supported Luther.
The Role of Women in Catholic and Protestant Churches
In both branches of Christianity, women have played significant roles, but there are differences in how they participate. In the Catholic Church, women serve as saints and religious missionaries, while in Protestantism, many women have been able to take on prominent roles in leadership and education. The role of Katharina von Bora, the wife of Martin Luther, is a notable example of this topic.
Influential Narratives and Stories in the History of Catholicism and Protestantism
The history of Christianity is filled with narratives and stories that emphasize the differences and similarities between these two branches. For example, the story of the Thirty Years’ War, which occurred between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most influential religious wars that began due to the conflict between Catholics and Protestants and had profound effects on European societies. This war not only reinforced doctrinal differences but also significantly impacted political and geographical transformations in Europe.
Specific Rituals and Ceremonies in Each Branch
In the Catholic Church, religious rituals and ceremonies are very extensive and rich. The Eucharist, baptism, confession, and holy matrimony are among the ceremonies that are performed with great care and specific details. In contrast, Protestants, depending on their denomination, have simpler ceremonies and place greater emphasis on individual spirituality and direct connection with God. This difference in how ceremonies are conducted reflects the different attitudes of these two branches toward the concept of worship and relationship with God.
Analysis of Social Movements Related to Protestant and Catholic
Social movements related to Protestants and Catholics also reflect the deep cultural and doctrinal differences between these two branches. The Puritan movement in England was an example of Protestant movements that sought social and religious reforms. This movement was known for its emphasis on simplicity and avoidance of corruption and luxury. On the other hand, the Jesuit movement in the Catholic Church was established to strengthen Catholic faith and counter Protestant reforms, playing an important role in promoting Catholic teachings worldwide.
The Role of Art and Architecture in Explaining Protestant and Catholic Differences
Art and architecture also played a key role in explaining the differences between Protestant and Catholic. Catholic churches, with their Gothic architecture and use of murals and sacred statues, glorified the sacred and attracted the attention of believers. In contrast, Protestant churches, due to their emphasis on simplicity and avoidance of any luxury, had simpler architecture and rarely used visual arts for decorating the church. These differences reflect the different views of these two branches on the concept of worship and sanctity.
 Comparison of the role of music in Protestant and Catholic churches
Comparison of the role of music in Protestant and Catholic churches The Role of Music in Protestant and Catholic Churches
Music is also another important aspect of the difference between Protestants and Catholics. In the Catholic Church, music, especially choral music and organ music, plays a prominent role in religious ceremonies. Music in the Catholic Church is performed to create a sacred atmosphere and emphasize the sanctity of the ceremonies. On the other hand, Protestant churches tend to prefer simpler and more accessible music for the general public. Congregational hymns sung by all church members are very common in Protestant ceremonies and are used as a way to enhance the sense of unity and participation in worship.
Religious Movements and Their Impact on the Modern World
Protestant and Catholic religious movements have had profound impacts on the development of the modern world. On one hand, the Protestant Reformation movement contributed to the formation of concepts such as religious freedom and individual rights, which ultimately led to the emergence of democratic governments in the West. This movement, by emphasizing the translation of the Bible into local languages, increased public literacy and broader access to sacred texts. On the other hand, the Catholic Church played an important role in scientific and cultural development by establishing universities and educational centers worldwide. These educational centers are recognized as one of the important factors in preserving and spreading knowledge during the Middle Ages and beyond.
Philosophical and Theological Differences between Catholic and Protestant
The philosophical and theological differences between Catholics and Protestants relate to various topics including divine grace, good works, and destiny. Catholics believe in the importance of good works and the cooperation of humans with divine grace for salvation, while Protestants adhere to the teaching of Sola Fide (salvation only through faith) and believe that a person can only be saved by faith in God. These differences in philosophy and theology have led to the formation of different views on salvation, life after death, and the role of the church in guiding the spiritual life of humans.
Comparison Table of Movements and Cultural Impacts
| Movement | Catholic | Protestant |
|---|---|---|
| Religious Reformation | Opposition to reforms and preservation of church traditions | Initiated by Martin Luther and emphasis on church reform |
| Religious Movements | Jesuit movement to strengthen Catholic faith | Puritan movement for social and religious reform |
| Art and Architecture | Use of visual arts to glorify the sacred | Emphasis on simplicity and avoidance of luxuries |
| Role of Women | Women’s roles mainly as nuns and missionaries | Wider roles in religious education and local leadership |
| Music | Choral and organ music to create a sacred atmosphere | Congregational hymns to enhance unity and participation |
| Impact on the Modern World | Establishment of universities and educational centers | Promotion of religious freedom and individual rights |
Long-term Effects of Protestant and Catholic Reformations
The Protestant Reformation had profound effects on European societies and even the world. On one hand, the emphasis on individual freedom and personal responsibility led Protestant societies towards scientific advancement and economic development. On the other hand, the Catholic Church, with its emphasis on church hierarchy and preservation of traditions, remained one of the important religious and cultural institutions. Additionally, the Catholic Church played a significant role in supporting the poor and needy through the promotion of charitable activities and social services.
The Role of Economy in the Development of Catholicism and Protestantism
One of the less examined aspects of the differences between Catholics and Protestants is the role of economy in the development of each of these branches. The Catholic Church, especially during the Middle Ages, was recognized as one of the wealthiest religious institutions in Europe, possessing extensive assets in the form of agricultural lands, gold, and artworks. This wealth allowed the church to play a prominent role in politics and economics and influence important governmental decisions.
In contrast, Protestantism significantly contributed to modern economic development by promoting values such as simplicity, hard work, and economic independence. Protestant economic theories, such as those described by Max Weber in “The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism,” greatly aided the formation of capitalism and economic development in the West. Protestants believed that work and effort were signs of divine blessing, leading Protestant societies towards greater development and economic success.
 Comparison of religious education between Catholic and Protestant
Comparison of religious education between Catholic and Protestant The Connection between Education and Religious Differences
The differences between Catholics and Protestants in education and teaching are also noteworthy. The Catholic Church has established large educational institutions and universities since the Middle Ages that focus on theology, philosophy, and art. These institutions have played an important role in transferring knowledge and preserving cultural and religious artifacts.
In contrast, Protestants, especially after the Reformation movement, placed great emphasis on public education and the translation of the Bible into local languages. This effort increased public literacy in Protestant communities and allowed people to study sacred texts themselves. This type of education strengthened critical thinking and independence in understanding religion and contributed to the cultural and social development of Protestant communities.
Differences in Attitudes towards Science and Philosophy
The attitudes of Catholics and Protestants towards science and philosophy are also among the important aspects of the differences between these two branches of Christianity. The Catholic Church historically played a significant role in supporting science and scientists, especially during the Renaissance. Many great scientists, such as Galileo and Copernicus, conducted scientific research within the framework of the Catholic Church, although some of this research faced resistance from the church.
In contrast, Protestantism, by emphasizing intellectual independence and rejecting religious authoritarianism, provided a more open space for the growth of science and philosophy. Many Protestant communities, particularly in England and Germany, engaged in the development of natural sciences and philosophy and played an important role in the Age of Enlightenment. This attitude led to the acceptance of new sciences and philosophy as tools for better understanding the world and connecting with God in Protestant communities.
Comparison Table of Economic, Educational, and Scientific Impacts
| Aspect | Catholic | Protestant |
|---|---|---|
| Economy | Focus on church wealth and prominent role in politics and economics | Emphasis on hard work, simplicity, and the formation of the spirit of capitalism |
| Education | Establishment of large universities and educational institutions to preserve religious and philosophical knowledge | Emphasis on public education and increasing literacy through the translation of sacred texts |
| Science and Philosophy | Support for science despite some limitations and resistances | Emphasis on intellectual independence and support for the development of science and philosophy during the Age of Enlightenment |
Conclusion
Although Protestants and Catholics adhere to the fundamental teachings of Christianity, there are profound differences in religious authority, church structure, religious rituals, and views on salvation and redemption. These differences primarily stem from the history of the Reformation movement and continue to influence the practical and doctrinal approaches of followers of these two branches.
For further reading on the differences and details of each branch, you can browse other articles on our website and also download this PDF article.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Difference between Protestant and Catholic
1. What are the fundamental differences between Protestant and Catholic?
The fundamental differences between these two branches include religious authority, religious rituals, the role of the church in religious life, and views on salvation and the Virgin Mary. Protestants believe in the principles of Sola Fide (salvation through faith) and Sola Scriptura (the Bible as the only source of truth), while Catholics rely on traditions and teachings of the church as valid sources.
2. What is the role of the Pope in the Catholic Church and do Protestants accept the Pope?
The Pope is the leader of the Catholic Church and serves as the spiritual leader of the church and Catholic Christians as the successor of Saint Peter. Protestants do not accept the Pope as a religious authority and believe that the only true source of faith is the Bible.
3. Are there differences in how religious ceremonies are conducted between Protestants and Catholics?
Yes, there are significant differences in how religious ceremonies are conducted. Catholics emphasize traditional rituals such as the Eucharist, baptism, and confession, while Protestants may conduct simpler and different ceremonies depending on their denomination.
4. How do Catholics and Protestants view salvation and redemption?
In Catholicism, salvation is achieved through faith in Christ, good works, and the performance of sacred rituals. In contrast, Protestants believe that salvation is possible only through faith in Jesus Christ and divine grace, and that good works do not play a role in salvation.
5. Do Protestants and Catholics differ in their interpretation of the Bible?
Yes, Catholics believe that the interpretation of the Bible should be guided by the church and the Pope, while Protestants believe that each individual can interpret the Bible personally (Sola Scriptura).
6. Do Catholics and Protestants conduct marriage ceremonies in the same way?
In the Catholic Church, marriage ceremonies are conducted with more elaborate rituals and are considered a sacred rite, while Protestants may have simpler ceremonies with less emphasis on church rituals.
7. Do Catholics and Protestants have different views on priests?
Yes, in the Catholic Church, priests act as intermediaries between God and believers, while in Protestantism, priests primarily serve as guides and teachers, with less direct mediation between God and believers.
8. Do Protestants accept the concept of intercession by saints?
No, Protestants believe that intercession is only performed through God and Jesus Christ and do not require the intercession of saints, while Catholics consider the intercession of saints to be valid.
9. What is the view of Catholics and Protestants on the Virgin Mary?
Catholics regard the Virgin Mary as the holy mother of Jesus Christ and hold her in high esteem, while Protestants accept Mary as the mother of Jesus but do not attribute any special sanctity or status to her.
10. What is the difference between Protestants and Catholics regarding good works?
Catholics believe that salvation is achieved through faith and good works, while Protestants believe that salvation is possible only through faith in Christ and that good works do not play a determining role in salvation.
11. Is the structure of the Catholic and Protestant churches the same?
No, the Catholic Church has a hierarchical structure with the Pope at the top, while the structure of Protestant churches is diverse, and many have a democratic structure.
12. What is the role of the Pope in the Catholic Church and do Protestants have a similar position?
The Pope is the leader of the Catholic Church and serves as the spiritual leader as the successor of Saint Peter. Protestants do not have a position similar to the Pope and emphasize individual and direct spiritual leadership with God.
13. What are the differences in religious rituals between Catholics and Protestants?
Catholic rituals include ceremonies such as the Eucharist, baptism, and confession, which are performed with care and specific details. Protestants, depending on their denomination, may conduct simpler rituals and some of these rituals may be held in a less formal manner.
14. Do Protestants and Catholics differ in their views on life after death?
Both branches believe in life after death, but Protestants emphasize salvation through faith in Christ, while Catholics also consider good works and the performance of sacred rituals important for salvation and redemption.





